System Validators
Validator Properties Dialog Box
Inclusive/Exclusive
Min/Max. value
Introduction
In addition to the field type and mandatory setting, system validators can be used to validate data entered by the user. Each field type has its own set of available validators, details of which can be found below. A field can be configured to use any of the validators available for its field type.
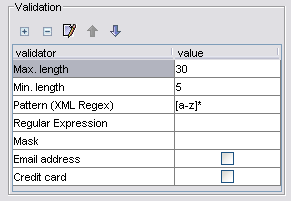
The grid shows both the available and configured validators for this field. In this example, the field has been configured with three validators. The first two ensure that field values contain between 5 and 30 characters. The third is a regular expression restricting field values to alphabetic characters. The value of any validator can be changed by editing the appropriate grid cell.
![]() -
add a new validator. This is only needed if
more than one validator of the same type is needed.
-
add a new validator. This is only needed if
more than one validator of the same type is needed.
![]() - removes a validator.
- removes a validator.
![]() -
edit the properties of a validator.
-
edit the properties of a validator.
![]()
![]() - changes the order that the validators
will be executed. Moves the selected validator up or down.
- changes the order that the validators
will be executed. Moves the selected validator up or down.
Validation can be performed on both the server and the client.
Client validation
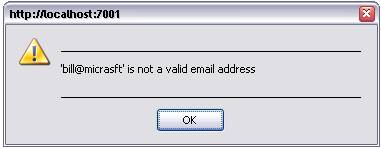
Client validation is written in javascript and executes on the user’s browser. If a client validator fails, a message box with a suitable error is displayed, prompting the user to enter a legal value. An error box will only be displayed for the first field to fail.
Example of a client validation failure
Server validation
Server validation performs the same job as client validation, but is executed on the server. If a validator fails, the error will be displayed in the page above the invalid field. Unlike client validation, an error is shown for all failures simultaneously.
Example of a server validation failure (showing part of the web page)

Validator Properties Dialog Box
Each validator can be configured by clicking
the ![]() button.
button.
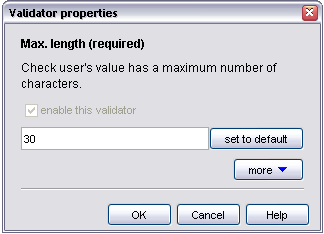
enable this validator - Select the checkbox to enabled this validator. If the validator needs a property value, it should be entered in the field.
set to default - This button will only show if a default value is available. Click the button to reset the value to the default value.
Use the more/less button to show and hide advanced properties.
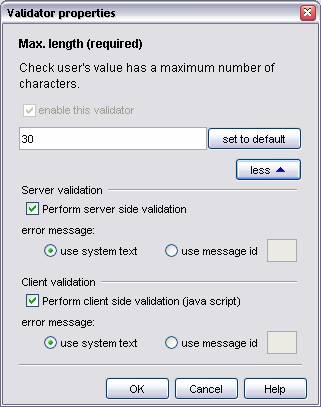
Use these properties to enabled/disable client and server validation. Client (javascript) validation will only occur if three conditions are satisfied.
- The "perform client side validation" check box must be selected.
- Javascript has not been disabled in the accessibility settings.
- The user's browser supports javascript.
error message: - choose the error message that is displayed when a validation check fails. It can either be a system text or a project message.
use system text - a global system text error message. Use the system texts editor to change this. (Tools -> System Texts Editor)
use message id - Enter the id of one of the project's messages.
The Validators
Max. Length
Field types: All types
The property value specifies the maximum number of characters that the field value can have.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
5 |
qwer |
qwerty |
|
5 |
qwert |
|
Min. Length
Field types: Character
The property value specifies the minimum number of characters that the field value can have.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
5 |
qwerty |
qwer |
|
5 |
qwert |
|
Max. Digits
Field types: Integer, Numeric, Currency
The property value specifies the maximum number of numeric digits characters that a field value can have. This is sometimes referred to as precision. Decimal points, minus signs, formatting characters and trailing zeros are all ignored in this check.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
5 |
12345 |
121233 |
|
5 |
1.2345 |
1.23456 |
|
5 |
-1.2345 |
-1.23456 |
|
5 |
1.234500 |
1.234501 |
|
5 |
1234 |
|
Pattern (XML Regex)
Field types: Character
User input is validated by performing a regular expression match against the provided pattern. This is a regular expression as specified in W3C XML Schema specification. (Part 2 section 4.3.4). An XML regular expression is similar to a Perl Regular Expression. The main difference is that expressions are matched against the entire user value. For this reason the expression should not start and end with ^ and $.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid value |
|
[a-z]+ |
asdfg |
as2dfg |
|
[a-z]+ |
abcdefg |
aBcdefg |
|
[a-zA-Z]+ road |
|
|
|
\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3} |
127.0.0.01 |
aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd |
|
123 |
123 |
b123 |
Note: The pattern validator has no client side check (javascript). User input errors will only be detected by server side validation.
Regular Expression
Field types: Character
User input is validated by performing a regular expression match against the provided pattern. In contrast to the pattern validator, this validator may match a subsection of the user value. If the whole value is to be matched, the pattern should start with a ^ and end with a $.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid value |
|
[a-z]+ |
QQQasdfgQQQ |
QQQQQQQ |
|
^[a-z]+$ |
abcdefg |
aBcdefg |
|
^[a-zA-Z]+ road$ |
|
|
|
[a-zA-Z]+ road |
|
|
|
^\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}$ |
127.0.0.01 |
aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd |
|
^123$ |
123 |
b123 |
Note: Server side validation uses java.util.regex.Pattern, which has been included with Java since version 1.4. Client side validation uses the Regex class included with javascript since version 1.2. Both of these are very similar to Perl regular expressions, however a few subtle differences do exist. Please refer to the relevant documentation for details.
Input mask
Field types: Character
This validator allows
specification of a mask to constrain which characters can be entered. The
following characters can be entered in the mask:
N
Any numeric digit 0 - 9
A
Any alphabetic digit A - Z
*
Any single character
-
Any group of characters
Any other character in the mask must exactly match
entered data (including the case).
The '-' mask character can only appear once in the
mask and it must be either the first or last character specified.
Examples:
|
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
NNA |
12B |
12$ |
|
NNA |
98H |
AAA |
|
NNA |
04z |
1A |
|
**A |
&&Z |
123 |
|
**A |
12B |
1Z |
|
|
1ZX |
1Z5 |
|
NNA78 |
12B78 |
12B77 |
|
NNA78 |
34s78 |
343434 |
|
A- |
A1234 |
1234 |
|
-NN |
ABC99 |
ABC3Q |
|
-NN |
QWERT00 |
QWERT |
Inclusive/Exclusive Min/Max. value
Field types: Integer, Numeric, currency, Date, Datetime, Time
These validators are useful for limiting the range of a field value. The inclusive validators check a field value up to and including the property value. The exclusive validators check a field value up to but not including the property value.
These validators, work on both numeric and date type fields. On the numeric style fields, numeric comparisons are performed (i.e. is 2.9 less than 3). On date and time fields chronological comparisons are performed (i.e. is 12:35 before 15:27).
The property value for Date, Datetime and Time checks should be entered in the format configured for server property date literal format.
Examples:
|
Field Type |
Validator |
Property value |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
Integer |
Max. Inclusive |
57 |
57 |
58 |
|
Integer |
Max. Exclusive |
57 |
56 |
57 |
|
Integer |
Min. Inclusive |
23 |
25 |
3 |
|
Integer |
Max. Exclusive |
23 |
10 |
77 |
|
Date |
Max. Inclusive |
31/12/1999 |
31/12/1999 |
1/1/2000 |
|
Time |
Max. Inclusive |
13:47 |
10:57 |
15:24 |
Decimal digits
Field types: Numeric, currency
Ensures that the number of decimal digits in the
user's value does not exceed the decimal digit setting for this
field. Each numeric field can be set with a rounding option and a
maximum decimal digit setting in the field
properties. If this validator is not
selected then the number will be silently rounded to the required decimal
digits. If this validator is selected
then it will be impossible for the user to enter excessive digits.
Examples:
|
Dec. Digit Setting |
Enabled |
Valid value |
Invalid Value |
|
3 |
No |
1.23456 |
None |
|
3 |
Yes |
1.234 |
1.2345 |
Email address
Field types: Character
Checks that the user's value is a valid email address, as specified by RFC 822. Only the format of an email address is checked and the presence of an active mailbox cannot be guaranteed.
Credit card
Field types: Character
Performs a Luhn check on the field value. A Luhn check is a numeric algorithm often used to quickly verify the validity of a credit card number. This cannot detect the presence of an actual account and certainly cannot authorize transactions.