The Ebase Xi Batch System
Internationalization
considerations
See also: Batch XML documents, Batch Administration
Overview
Batch processing is the ability of the system to process
forms supplied in XML format in "unattended" mode i.e. with no end
user. Each XML document or batch can consist of any number and
type of forms. XML documents can be read either from a file system or via a
URL. Forms are processed as if an end user were present: processing starts from
the first page and continues until there are no more pages to process. All
events and associated script processing is handled the same as for online
users. If an error occurs, the form is marked as 'error' and processing
continues with the next form in the batch. Each executed batch produces a
response XML file which can be returned to the caller and can also be displayed
using the Server Administration Application.
The batch system is a legacy feature and doesn’t support all aspects of form behaviour. In particular, there is no support for: tables, buttons, hyperlinks.
The batch system is administered using the Server Administration Application and
provides the ability to:
·
Display all batches showing their status
·
Display input XML documents
·
Display XML output documents
·
Re-run failed batches
·
Change the status of a batch
·
Schedule batch
processing at specific times
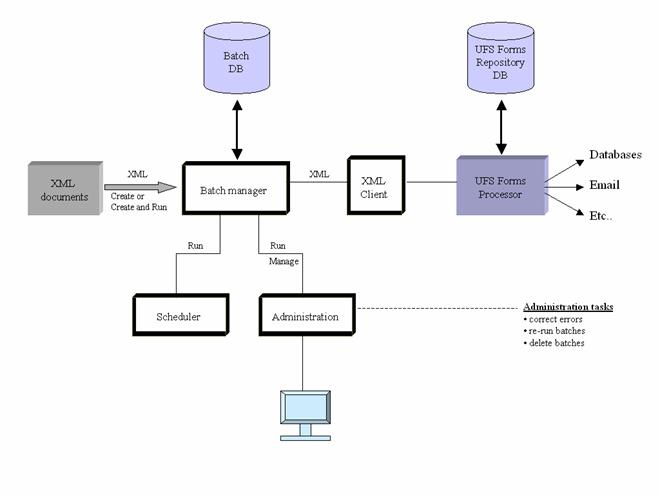
Architecture
The batch architecture is shown in the following diagram.
The XML
client component processes one form at a time, taking a XML document as input
and returning a response XML document. This component can also be called
interactively if required, but documentation on this is not included. If you
would like to use this facility, please contact support@ebasetech.com.
Processing options
Each input XML document contains a batch header which
specifies whether the batch should be executed immediately or simply stored in
the database for later execution, via either the scheduler or the batch
administrator. If the caller is interactive, i.e. via URL as opposed to a file,
the batch manager will return a XML response document. This will be a
full response if immediate execution has been requested or a simple
acknowledgement if the batch has been stored but not yet executed. (See Batch XML Documents for more information)
Each batch has a name, which is supplied in the input XML
document, and is also assigned a unique id by the system. Batch execution via
the Scheduler allows the specification of masked names: e.g. Order* for all
batches with names beginning with 'Order' or simply * to signify all batches.
Scheduled execution also provides an option for re-execution of batches with an
error status.
When a batch with an error status is re-executed, either
via the scheduler or via the Server Administrator, only those forms which had
previously failed are re-executed, and successful forms are ignored.
Internationalization
considerations
For certain Ebase field types e.g. date and numeric
fields, the format in which the input data is supplied is dependent on the
language in which the form is to be executed. The runtime language can be
specified for each form within a batch using the language attribute on
the <Form> tag for the form e.g.
<Form
id="TEST" language="NL">
In this example, input data will be treated as having the
format applicable for language NL e.g. 25-07-2004 is a valid format for a date
field, 25/07/2004 is invalid; 11,76 is a valid currency format, 11.76 is
invalid.
If a language is not specified for the form, the system’s
default language is used.
The required formats for input data for each language can
be determined from the language page in the Server
Administration Application, then viewing the properties of the language.
The required date and numeric formats are displayed in the Format panel.
(See Internationalization Support
for more information)
Sending XML interactively
As described above, XML input documents can be sent to the
Ebase Xi server interactively and the system will return a XML response
document. The Java servlet name is BatchServer and therefore the full URL will be www.domain.com/ufs/BatchServer
(though this may be configured differently).